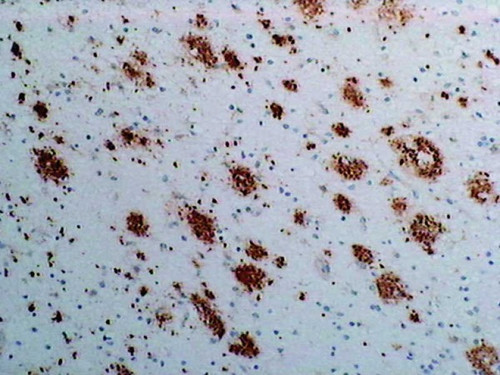
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the presence of extracellular plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in the brain. The major protein component of these plaques is beta amyloid (Aβ) peptide, a 40 to 43 amino acid peptide cleaved from amyloid precursor protein by β-secretase and γ-secretase. Increased release of Aβ42 or Aβ43, both of which exhibit a greater tendency to aggregate than Aβ40, occurs in individuals expressing certain genetic mutations, ApoE alleles or may involve other undiscovered factors. Many researchers theorize that it is this increased release of Aβ42/Aβ43 which leads to the abnormal deposition of Aβ and the associated neurotoxicity in the brains of affected individuals. It is also reported that a distinct Aβpeptide, AβN3pE, is deposited in senile plaques in a dominant and differential manner as compared with the standard Aβpeptide. For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedures.
- application:
- IHC, WB
- Catalog number:
- 18582-S
- Datasheet:
- formulation:
- Lyophilized product in PBS containing 1 % BSA and 0.05 % NaN3
- immunogen:
- Synthetic peptide of a C-terminal part of Human Amyloidβ42
- notes:
- For research use only, not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The datasheet for this product (see above) is intended to serve as an example only. Please refer to the datasheet provided with the antibody for precise details. - Other names:
- Aβ, Amyloid beta, A-beta
- Protocol:
- purification:
- Affinity Purified with synthetic peptide
- size:
- 5 µg
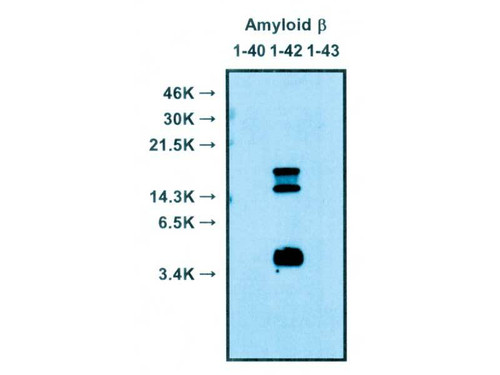
- specificity:
- Human Amyloid Beta Aβ 42 specific. Not cross-react with Human Amyloid Beta Aβ 40 or 43.
- storage:
- Lyophilized product, 5 years at 2 - 8°C; Solution, 2 years at -20°C.
- Species:
- Human
- Host:
- Rabbit
- Additional info:
- References: